4Cs
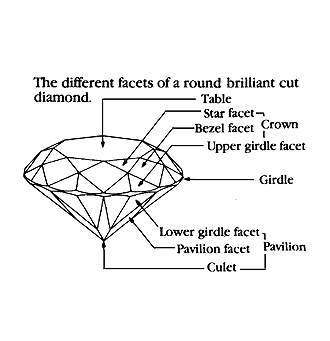
CUT
When we speak of cut we are more interested in the proportions of the diamond as opposed to its shape (Round Brilliant, Marquise, Pear, Princess, etc.)
Every diamond regardless of its shape gets it brilliancy and scintillation by cutting and polishing the diamond facets to allow the maximum amount of light that enters through its top to be reflected and dispersed back through its top.
A correctly cut, "well made", stone is pictured in diagram.
As you can see if the angles are correct the light that enters is dispersed properly back through the diamond's top facets.
When a stone is cut too shallow or too deep the light that enters through the top is allowed to escape through the diamond's bottom and does not allow the maximum beauty of the diamond to be realized.
CARAT-WEIGHT
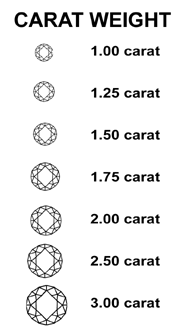
This is the weight of a diamond measured in carats. As the carat weight of a diamond increases so does its rarity and therefore its price.
One carat is divided into 100 "points," so that a diamond of 75 points weights .75 carats. The carat-weight of a diamond is the easiest measurement to determine. Most importantly, two diamonds can be of equal carat-weight, but their value can differ greatly due to their cut, color, and clarity.
COLOR
Diamonds come naturally in every color of the rainbow. However most people are concerned with diamonds in the white range. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) rates the body color in white diamonds from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow).
The best color for a diamond is no color at all. A totally colorless diamond allows light to pass through it easily, resulting in the light being dispersed as the color of the rainbow. Colors are graded totally colorless to light yellow. The differences from one grade to the other are very subtle and it takes a trained eye and years of experience to color grade a diamond.
CLARITY
The clarity of a diamond is determined by the amount and location of flaws, or blemishes, in the diamond when viewed under 10 power (10x) magnification. GIA rates clarity grades in diamonds from Flawless to Imperfect 3 (see chart below). The Diamond Shopping Network offers you diamonds from the Imperfect 1 grade through Flawless.
Most diamonds contain very tiny birthmarks known as "inclusions." An inclusion can interfere with the light passing through the diamond. The fewer the inclusions, the more beautiful the diamond will be.
ABOUT MINED DIAMONDS
MINED DIAMONDS
Diamonds are symbols of enduring beauty and love. But they often have a dark side that stands in direct contrast to this beauty.
This is because the majority of diamonds on the market are mined at an incredible cost to the communities and environments that harbor them. While all forms of mining can have negative consequences, diamond mining has proven especially brutal.


ETHICAL IMPACT
It is no secret that the quest for diamonds has contributed to human suffering. The impact has been especially severe in Africa, which contains much of the world’s natural diamond supply. Over the last decade, consumer awareness of the diamond trade’s harsh practices has grown. In-depth reporting and even popular culture movies like Blood Diamond have shed light on how it fuels forced labor, violence and countless casualties.
While the mined diamond industry seeks to address some of these issues through increased transparency around the source of diamonds, it cannot fully eradicate them. In fact, it is estimated that about 5-10% of the world’s diamonds are still illegally traded1. Since raw diamonds exchange hands many times after their discovery, the risk remains that a mined diamond may still be associated with some conflict. But even if the industry could somehow fully eliminate these ethical risks, there is another looming casualty to consider: the environment.
ECOLOGICAL IMPACT
Diamond mining can devastate environmental ecosystems. Here are a few examples of how the most popular techniques wreak ecological havoc.
▶ Marine mining, commonly practiced today, deploys large ships with powerful pipes that often drill deep into the seabed to reach diamond deposits. The pipes indiscriminately suck up everything in their path, displacing and disrupting the sea life.
▶ Open pit mining, one of the oldest techniques, requires digging miles beneath the earth’s surface. The process can displace about 1,700 tons of earth for a one carat rough diamond. This leads to deforestation, soil erosion and the depletion of precious farmland.
▶ Alluvial mining employs walls and dams that redirect water flow to capture diamonds that have reached the surface of river beds after years of natural erosion. This impacts the quality of the water and the health of aquatic life.
WHY COMPROMISE?
Over the last decade, technological advances in lab made diamond creation have made it possible to match the quality found in nature – to the point that trained gemologists cannot tell the difference between a mined and a lab grown diamond of comparable features. After years of human suffering and ecological devastation, it is worth pausing to question why there would ever be a good reason to purchase a mined diamond. There isn’t.
With a certified Lab Created diamond, you don’t have to compromise between quality and ethics. You get both a perfectly beautiful diamond and the peace of mind that it truly is clean, free of conflict and friendly to the environment. And if that wasn’t enough, it also happens to be friendly to your wallet! Clean Origin Lab Created diamonds can be up to 40% less expensive than their comparable mined counterparts.
In 1477 the Archduke of Austria started a tradition that has endured through the ages – the romantic gesture of offering a diamond engagement ring. It’s about time a diamond’s origin matched this beautiful sentiment. At Clean Origin, we believe true love deserves nothing less.
ABOUT LAB GROWN DIAMONDS
WHAT IS A LAB CREATED DIAMOND?
The number one question we get is “Are lab-created diamonds real diamonds?” (also called man-made or lab-grown)
The answer is a very simple yes.
The only thing that makes a lab-created diamond different from a natural is diamond is its origin. A lab-created diamond is “grown” inside a lab using cutting-edge technology that replicates the natural diamond growing process. The result is a diamond that is chemically, physically, and optically the same as those grown beneath the Earth’s surface.
“[Lab-created diamonds] are not fakes. They’re not cubic zirconias. They have all the same physical and chemical properties of a mined diamond.” Stephen Morisseau, a spokesman for the Gemological Institute of America, a nonprofit organization that oversees the international diamond grading system.
Sometimes, lab-created diamonds are referred to as synthetic diamonds. While not technically inaccurate, term “synthetic” may be the reason people believe lab-created diamonds are “fake.”
If we compare them to other popular diamond simulants, it’s obvious they are, in fact, the real deal.

